Low-code platforms: Efficient process design for banks and insurance companies
Published April 13, 2024
- Banking
- Insurance

Banks and insurance companies are currently facing intense competitive pressure from new product launches, regulatory changes and evolving hybrid customer behavior. The diversity of potential customer touch points continues to grow, driving demand for digital solutions in particular. To meet these changing customer demands, financial services organizations must streamline processes and continuously monitor and improve the customer experience.
Low-code platforms: a modular building block system
In recent years, the use of low-code platforms has gained increasing popularity as a means to create more efficient and customer-centric processes. Low-code platforms enable companies to quickly and easily create and customize tailored applications without extensive programming knowledge. A low-code system can thus be viewed as a highly modular building block system that offers the ability to construct custom applications – such as application processes in the financial services industry – using pre-built blocks and components.
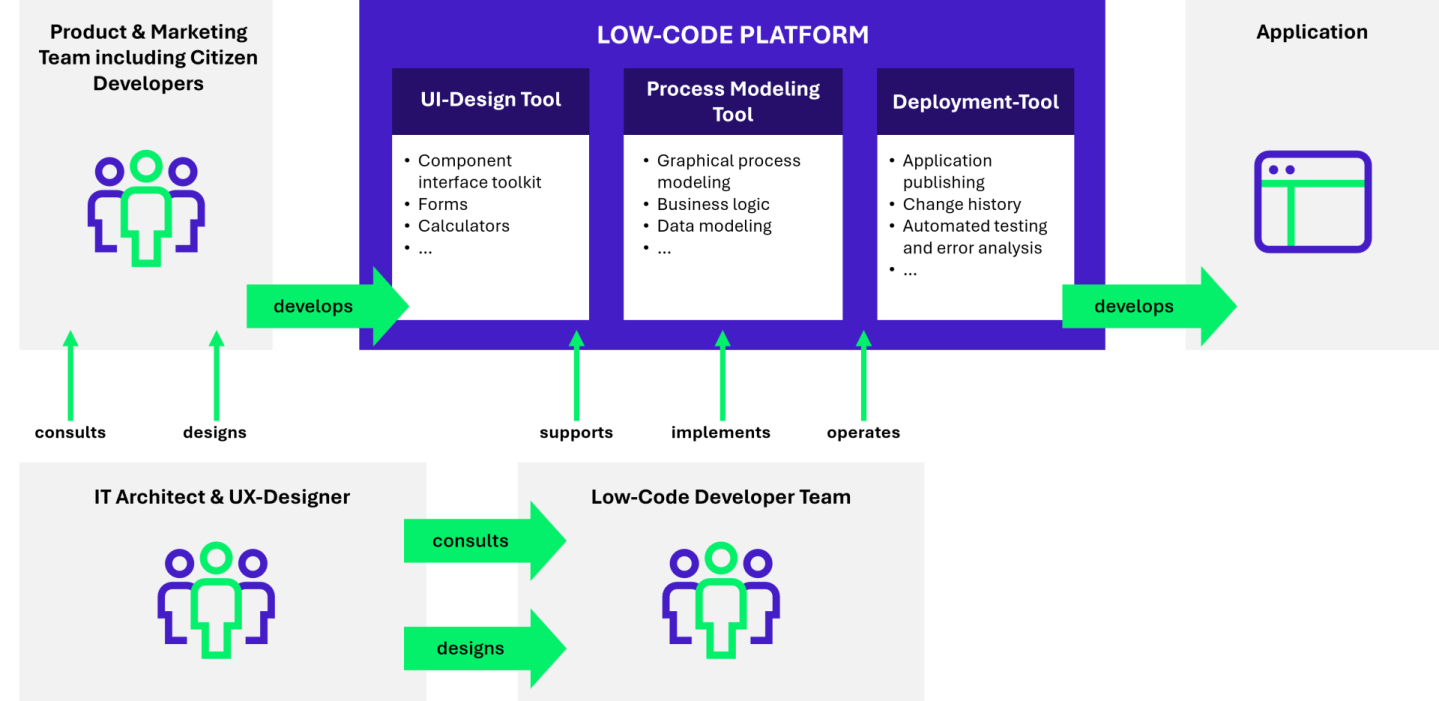
Configure instead of code
A low-code system can be operated by so-called citizen developers. The foundation for this is training for employees from business units that conveys basic IT system knowledge and teaches people how to work with the low-code system. Advanced programming skills are not required. Through training, citizen developers become capable of implementing applications, including business logic, in a low-code system. Furthermore, they can independently launch and operate these applications. The result is significantly shorter implementation times, which in practice accelerates the development of different variants of application processes, for example.
Maximum Flexibility, Speed, and Time-to-Market
A low-code solution offers companies maximum flexibility in rapidly modifying and optimizing individual components of an application. With a modular application architecture, sales and service applications or MVP solutions can be flexibly adapted or even rebuilt from scratch.
Explanation of MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
An MVP is a product or service that contains only the essential features needed to solve the identified customer problem. The aim of launching an MVP is to get early feedback on the solution during the development process and make improvements accordingly.
Beyond this increased flexibility, speed is another key benefit of low-code solutions. Thanks to the intuitive user interface, applications or prototypes can be developed much faster than with traditional programming methods. Combined with continuous tracking of user behavior and bounce rates, this enables user- and customer-centric actions while progressively optimizing the conversion rate. This shortened time-to-market allows companies to act faster and gain a competitive advantage, which is particularly important given the constant introduction of new products and services by FinTechs, InsurTechs and competitors.
Rapid Optimization of Conversion Rate
The efficiency and responsiveness benefits of low-code platforms are particularly valuable in areas where customer needs are changing rapidly, typically faster than traditional IT development cycles. For example, the changing expectations of specific audiences for digital application processes can put previously stable conversion rates through digital channels at risk. This not only leads to lost revenue, but also to a lower return on investment for any marketing campaigns aimed at these groups.
An example
A checking account for young adults is promoted through a social media advertising campaign. While the campaign generates significant attention, it results in few new account openings. Instead, tracking systems show high bounce rates, indicating that many people are dropping out during the application process. So how do you ensure that potential customers don’t give up in frustration just before they complete the account opening process? With a low-code platform, you can create and test modern, target group-optimized user interfaces with minimal effort and independently optimize the entire customer experience. By consistently analyzing and evaluating user behavior, each step of the application process can be continuously improved.
Rapidly expand your product portfolio from an IT perspective
Low-code is not just for quick UI optimizations. Current disruptions, such as those in the e-mobility space, demonstrate the need for insurers’ product development and IT to respond quickly to changing conditions. For example, with the introduction of e-scooters, insurers have been able to expand their motor insurance product portfolio to include liability and collision coverage specifically for e-scooters and integrate it into the application process. These rapid adaptations are also relevant to other technologies: drones require insurance coverage, and product spin-offs such as customized bicycle insurance require constant adaptation. The technical effort required in traditional systems is considerable. With low-code, implementation can be greatly accelerated. Depending on the complexity of the product, going live with a redesigned application process can be achieved within a few weeks.
Save costs and resources with low-code platforms
By using low-code platforms, organizations can save valuable IT resources and associated costs over the long term. Once the platform has been set up by a team of developers, the workload for optimizing and customizing applications is significantly reduced, allowing financial services organizations to make more efficient use of their IT budgets and free up technical expertise for other strategic projects.
However, it is important not to underestimate the need for IT and business to work hand in hand, especially in relation to platform integration. Different requirements are needed for the variety of business use cases and approaches to implementing low-code. Programming skills are needed to set up and maintain the platform, plus interfaces, customization, or database connectivity. After successful implementation, the benefits of the low-code system are realized through ease of use by citizen developers.
UX designers remain critical
What citizen developers typically lack is the expertise of IT architects and UX designers. An IT architect plans and builds applications according to best practice approaches aimed at maintainability and flexibility. If these approaches are ignored, even a low-code system can be “built” in a way that makes it stagnant and blocks further development. Negative effects become even more apparent when UX designers are omitted. A user’s experience with application processes has a direct impact on conversion and completion rates. If low-code applications appear unintuitive, confusing, or even frustrating, users will become dissatisfied and abandon the application before completion. The work of UX designers enables positive experiences and emotions for customers. Therefore, a team of business professionals and citizen developers should regularly consult with IT architects and UX designers on their projects for advice, optimization, and support.
Custom Development vs. Standard Solution
In the insurance and banking environment, numerous customer data points are processed, rates are calculated, and validations are performed. For these activities, core systems typically need to be connected to a low-code system through technically complex implementations before going live. Given this complexity, can a low-code system really work? Is custom development more appropriate, or can an off-the-shelf solution be used?
Today, various low-code platforms often come with connectors for standard software. The key is to ensure that the technology is optimized for the industry in question to minimize the need for customization of the off-the-shelf solution. However, depending on the specific business use case, custom development may make sense. This must be carefully evaluated in advance to ensure a successful and accurate solution. An important evaluation criterion can be, for example, the easy integration of third-party services through interfaces with internal IT applications. Services that recur frequently and automatically replace existing manual processes are particularly suitable. Examples include identification processes or credit scoring services.
The following questions will help you choose the right low code platform:
- What are the most promising use cases in terms of IT resource optimization and customer satisfaction?
- What data and integrations with existing IT systems are needed for the different possible applications?
- Where are the potential “low-hanging fruits”?
- Which low-code platforms best fulfill the individual requirements?
- How do the platform costs compare to the savings?
- What expansion and scaling capabilities does the platform offer?
- How should direct user feedback be incorporated?
Looking to the future
The rapid evolution of low-code platforms has fundamentally changed the way applications are developed. But what does the future hold? One promising prospect is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs). This fusion opens up new possibilities for application development, promising seamless user interaction and intelligent conversations.
On the one hand, AI can support programming by automating code generation, thereby increasing the speed and efficiency of platform expansion or maintenance. On the other hand, AI can also be used to review existing code for errors or potential improvements. Depending on the insurer’s needs, IT resources can be used more efficiently and processes can be continuously optimized. Text-to-code technology, which automatically translates business requirements and rules from natural language into lines of code, is already showing great promise.
Implementing LLMs such as Chat GPT at touch points along the customer journey of application processes creates entirely new use cases to better serve customer needs. A combination of speech-to-text frameworks (e.g. AWS Polly) that convert spoken words to text, and voice bots that create much higher quality customer communications through natural language via LLM, can create a new customer experience in low-code application processes.
Low code: A promising approach
Low-code is a promising solution to successfully meet market challenges. The building block principle of low-code platforms enables a modular application architecture that can be easily adapted and offers companies the opportunity to operate in a highly customer-centric manner. With an intuitive user interface, business and marketing professionals can create and optimize new sales and service applications to quickly improve the customer experience.
Overall, low-code is a powerful tool that can help banks and insurance companies work more efficiently, reduce costs over the long term, and position themselves competitively in a fast-paced marketplace.